PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
120 C (Decomposes)
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
The first chemical contrast of thiols and sulfides with alcohols and ethers is acidity which is important in organic reactions. Thiols are stronger acids than relevant alcohols and phenols. Thiolate conjugate bases are easily formed, and are excellent nucleophiles in SN2 reactions of alkyl halides and tosylates. The nucleophilicity of sulfur is much greater than that of oxygen, resulting in a number of useful electrophilic substitution reaction that are rare by oxygen. For example, sulfides form (with alkyl halides) ternary sulfonium salts, in the same alkylattion of tert-amines quaternary ammonium salts, whereas ternary oxonium salts are prepared only under extream conditions. Without exception, sulfoxides, sulfinate salts and sulfite anion also alkylate on sulfur, despite of the partial negative formal charge on oxygen and partial positive charge on sulfur. The second character is the oxidation states of sulfur. Oxygen has only two oxidation states, whereas sulfur covers from –2 to +6 as follows:
- -2: Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), sulfides, sulfonium ions
- -1: disulfides
- 0: S elemental, sulfoxides, sulfenic acids
- +2: sulfones, sulfinic acids
- +4: sulfonic acids, sulfite esters
- +6: sulfate esters
One more sulfur compound's contrast with oxygen analog is in oxidation chemistry. Oxidation of sulfur compounds changes the oxidation state of sulfur rather than carbon, whereas, oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones changes the oxidation state of carbon not oxygen. Thiols is oxidized to S-S single bond (disufide) which is stronger than O–O bond in peroxide. Disufide forms sulfenyl chlorides (with chlorine in mild condition) or sulfonic acids under harder condition. Oxidation of sulfides with hydrogen peroxide (or peracids) yields sulfoxides and then to sulfones. A certain sulfoxide compound such as dimethyl sulfoxide can be used as an effective oxygen source in the oxidation reaction of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. DMSO easily is reduced to dimethyl sulfide and water is taken up by the electrophile. oxidation procedure is very mild and tolerates a variety of other functional groups, including those having oxidizable nitrogen and sulfur atoms.
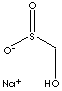
Sulfinic acid is an organic compound containing -SO2H group which is bonded to a carbon atom. Hydroxy methanesulfinic acid is used as a strong discharge medium of dyes and pigments. It is a strong reduction agent for textile printing. It is used in emulsion polymerisation process.APPEARANCE
98.0% min (Dihydrate)